

Doin' the Robot
(voice)
Vocoder
Why Web Audio? We have <audio>!
<audio controls preload="auto"
src="sounds/laser.ogg"></audio>
- Precise timing of lots of overlapping sounds
- An audio pipeline and routing system for effects and filters
- Hooks to visualize and manipulate audio data on the fly:
Intro to the Web Audio API
- High-level API, easy to use for basic tasks like
function playSound( buffer ) { var sourceNode = audioContext.createBufferSource(); sourceNode.buffer = buffer; sourceNode.connect( audioContext.destination ); sourceNode.noteOn(0); } - Effects and filters that don't require low-level knowledge of audio DSP
var delayNode = audioContext.createDelayNode(); delayNode.delayTime.value = 0.5;
- Low-level API for custom audio processing directly in JavaScript
- Native processing using separate high-priority thread to resist glitching
Web Audio Design Goals - Glitch-free
Audio Features Used in Gaming
- Very precise timing of many simultaneous sounds
- 3D spatialization - positioning sound at a particular place
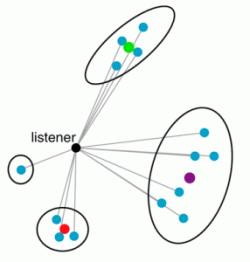
- Doppler shift - changing pitch for moving sources
- Distance attenuation and sound directionality
- Filtering effects (radio, telephone, etc.)
- Acoustic environments (reverb)
- Time-based event Scheduling
- create sequences / rhythms / loops
- fade-ins / fade-outs / sweeps
Audio Features Needed for Music Applications

- Oscillators - basis of synthesis
- Dynamics processing (compression)
- Waveshaping (non-linear distortion)
- Frequency and waveform analysis
Demo
The Web Audio API is Based on a Node Graph
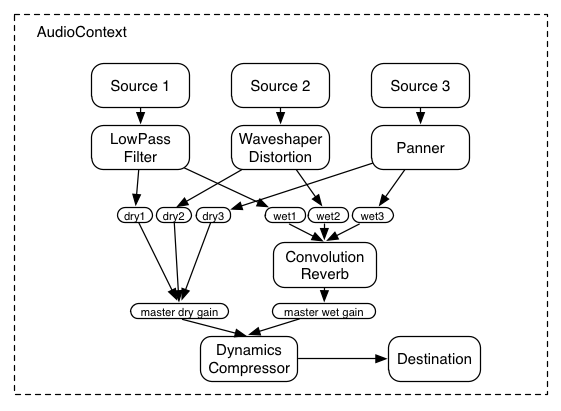
The Basics - AudioContext
interface AudioContext {
AudioDestinationNode destination; // the “speakers”
float sampleRate;
float currentTime;
AudioBuffer createBuffer( long numberOfChannels, long length, float sampleRate);
AudioBuffer createBuffer( ArrayBuffer buffer, boolean mixToMono);
void decodeAudioData( ArrayBuffer audioData, AudioBufferCallback successCallback,
AudioBufferCallback errorCallback);
// AudioNode creation
AudioBufferSourceNode createBufferSource();
AudioGainNode createGainNode();
DelayNode createDelayNode( float maxDelayTime );
BiquadFilterNode createBiquadFilter();
...
}
Creating an AudioContext
var audioContext = new webkitAudioContext;
The Basics - AudioNode
interface AudioNode {
void connect( AudioNode destination, [Optional] unsigned long output,
unsigned long input );
void connect( AudioParam destination, [Optional] unsigned long output );
void disconnect( [Optional] unsigned long output );
AudioContext context;
unsigned long numberOfInputs;
unsigned long numberOfOutputs;
}
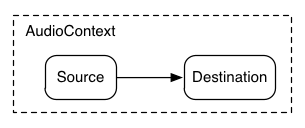
source.connect( destination );
The Basics - AudioParam
AudioParams let us do interpolation and scheduling under the covers
interface AudioParam {
attribute float value;
// Parameter automation
void setValueAtTime( float value, float time );
void linearRampToValueAtTime( float value, float time );
void exponentialRampToValueAtTime( float value, float time );
void setTargetValueAtTime( float targetValue, float time, float timeConstant );
void setValueCurveAtTime( Float32Array values, float time, float duration );
void cancelScheduledValues( float startTime );
}
The Basics - AudioBuffer
AudioBuffer represents a decoded, in-memory buffer of sound data
interface AudioBuffer {
float sampleRate; // in Hz
long length; // in samples
float duration; // in seconds
int numberOfChannels;
Float32Array getChannelData( unsigned long channel );
}
The Basics - AudioBuffer
You can access the data directly...
function loadNoiseBuffer() { // create a 2-second buffer of noise
var lengthInSamples = 2 * audioContext.sampleRate;
noiseBuffer = audioContext.createBuffer( 1, lengthInSamples, audioContext.sampleRate );
var bufferData = noiseBuffer.getChannelData( 0 );
for (var i = 0; i < lengthInSamples; ++i) {
bufferData[i] = (2*Math.random() - 1); // -1 to +1
}
}
AudioBuffer in Action
var dogBarkingBuffer = null;
var audioContext = new webkitAudioContext();
function loadDogSound(url) {
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open("GET", "dogBarking.mp3", true);
request.responseType = "arraybuffer";
request.onload = function() {
audioContext.decodeAudioData(
request.response, function(buffer) {
dogBarkingBuffer = buffer;
// buffer is now ready!
} ); }
request.send();
}
The Basics - AudioBufferSourceNode
One-shot playback of an AudioBuffer
- Multiple ABSNs can point to the same AudioBuffer!
interface AudioBufferSourceNode : AudioSourceNode {
// Many sources can share the same buffer
AudioBuffer buffer;
AudioParam playbackRate;
boolean loop;
void noteOn( double when );
void noteOff( double when );
void noteGrainOn( double when, double grainOffset, double grainDuration );
}
AudioBufferSource AND AudioBuffer in Action
var dogBarkingBuffer = null; var audioContext = new webkitAudioContext();
function loadDogSound(url) {
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open("GET", "dogBarking.mp3", true);
request.responseType = "arraybuffer";
request.onload = function() { audioContext.decodeAudioData( request.response,
function(buffer) { // success! we have a decoded buffer!
dogBarkingBuffer = buffer;
bark(); } ); }
request.send();
}
function bark() {
var dog = audioContext.createBufferSource();
dog.buffer = dogBarkingBuffer;
dog.connect( audioContext.destination );
dog.noteOn(0);
}
AudioBufferSource Looping
var dogBarkingBuffer = null;
function bark() {
var dog = audioContext.createBufferSource();
dog.buffer = dogBarkingBuffer;
dog.loop = true;
dog.noteOff( audioContext.currentTime + 600.0 ); // She stops after 10 minutes.
dog.connect( audioContext.destination );
dog.noteOn(0);
}

"Time" in the Web Audio API
- Time values in Web Audio are in SECONDS, not milliseconds
- Use
audioContext.currentTimeto get the time - This clock starts at zero when the context is created
- Be careful - the system clock may run at a different rate
Beyond the Basics
request.onload = function() {
audioContext.decodeAudioData(
request.response, function(buffer) {
dogBarkingBuffer = buffer;
bark(); // you don't usually immediately play this
}
);
}
But that's not all...
AudioNodes for Processing
- Gain control
- Delay effects
- Biquad Filters (low-pass, high-pass, bandpass, etc.)
- Panners (Spatialization)
- Convolution (reverb and other environmental effects)
- And more!

MediaElementAudioSourceNode
Integrate <audio> and <video> elements into the Web Audio pipeline
<audio id="audioTagID" src="longfile.ogg"></audio>
<script>
var audioContext = new AudioContext();
function setupStreamingSource() {
var audioElement = document.getElementById( 'audioTagID' );
var sourceNode = audioContext.createMediaElementSource( audioElement );
sourceNode.connect( gain1 ); // connect this whereever you want!
}
</script>
AudioGainNode - Volume Control
interface AudioGainNode : AudioNode {
AudioGain gain; // This is an AudioParam
}
AudioGainNode for Routing and Submixes
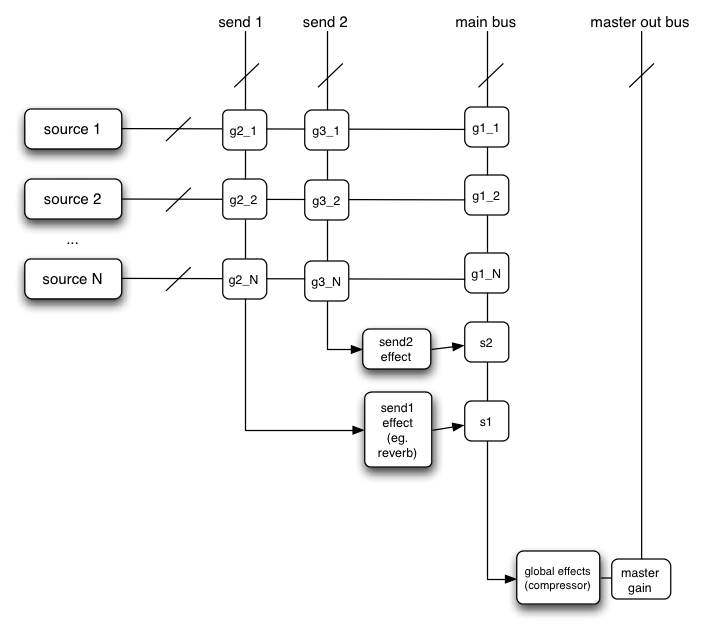
Implicit Mixing at AudioNode Connections!
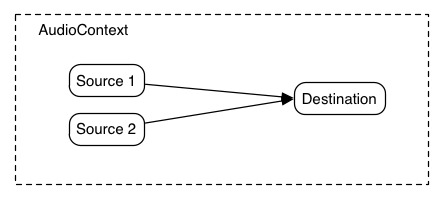
- Mixing happens automatically on nodes
- AudioParam inputs are also mixed
- Outputs can also fan out to many inputs
var dog = audioContext.createBufferSource(); var cat = audioContext.createBufferSource(); dog.buffer = dogBarkingBuffer; cat.buffer = catBarkingBuffer; dog.connect(audioContext.destination); cat.connect(audioContext.destination); dog.noteOn(0); cat.noteOn(0);
AudioGainNode Automation
Since gain is an AudioParam, you can do
var envelope = audioContext.createGainNode(); mySoundNode.connect( envelope ); envelope.connect( audioContext.destination ); var now = audioContext.currentTime; envelope.gain.setValueAtTime( 0, now ); envelope.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime( 1.0, now + 2.0 ); envelope.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime( 0.0, now + 4.0 ); mySoundNode.noteOn(0);
DelayNode
This node delays the audio signal passing through it
interface DelayNode : AudioNode {
AudioParam delayTime;
}
DelayNode
delayTime is an AudioParam!
interface DelayNode : AudioNode {
AudioParam delayTime;
}
var delayNode = audioContext.createDelayNode();
delayNode.delayTime.setValueAtTime(0.0,now);
delayNode.delayTime.linearRampToValueAtTime( 0.5, now + 4 );
soundNode.connect( audioContext.destination );
soundNode.connect( delayNode );
delayNode.connect( audioContext.destination );
soundNode.noteOn(0);
Also useful for flange and chorus effects.
RealtimeAnalyserNode
interface RealtimeAnalyserNode : AudioNode {
void getFloatFrequencyData( Float32Array array ); // grab frequency analysis (float)
void getByteFrequencyData( Uint8Array array ); // grab frequency analysis (uint8)
void getByteTimeDomainData( Uint8Array array ); // grab waveform data
unsigned long fftSize; // how detailed an analysis you want
float smoothingTimeConstant; // how much to average "frames"
}
What's the Frequency, Kenneth?
Frequency buckets are spread linearly across [0 , audioContext.sampleRate/2]
var analyser = audioContext.createAnalyser();
analyser.fftSize = 1024;
soundInput.connect(analyser);
analyser.connect(audioContext.destination);
function updateVisualizer(time) {
var freqByteData = new Uint8Array( analyser.frequencyBinCount );
analyser.getByteFrequencyData( freqByteData );
// Now you have an array of Uint8 values, representing the frequency band energy
// across analyser.frequencyBinCount bands. Do something cool with it!
for (var n=0; n<analyser.frequencyBinCount; n++)
doSomethingCool( freqByteData[ n ] );
window.webkitRequestAnimationFrame( updateVisualizer );
}
BiquadFilterNode
interface BiquadFilterNode : AudioNode {
const LOWPASS = 0, HIGHPASS = 1, BANDPASS = 2, LOWSHELF = 3,
HIGHSHELF = 4, PEAKING = 5, NOTCH = 6, ALLPASS = 7;
attribute unsigned short type;
readonly attribute AudioParam frequency; // in Hertz
readonly attribute AudioParam Q; // Quality factor
readonly attribute AudioParam gain; // in Decibels
}
Analysing Filters
Resonant Filter Sweep
var filter = audioContext.createBiquadFilter();
filter.type = filter.LOWPASS;
filter.frequency = 0;
filter.Q = 0;
// sweep the frequency from 0-5k; sweep the Q from 20 to 0.
var now = audioContext.currentTime;
filter.frequency.setValueAtTime( 0, now );
filter.frequency.linearRampToValueAtTime( 2000.0, now + 2.0 );
filter.frequency.linearRampToValueAtTime( 0.0, now + 4.0 );
filter.Q.setValueAtTime( 20.0, now );
filter.Q.linearRampToValueAtTime( 10.0, now + 4 );
Talking on the Telephone
var lpf = audioContext.createBiquadFilter(); lpf.type = lpf.LOWPASS; lpf.frequency.value = 2000.0; input.connect( lpf ); var hpf = audioContext.createBiquadFilter(); hpf.type = hpf.HIGHPASS; hpf.frequency.value = 500.0; lpf.connect( hpf ); hpf.connect( out );
AudioPannerNode
Position sounds in the 3D sound field- great tutorial on HTML5Rocks.
AudioPannerNode Interface
interface AudioPannerNode : AudioNode {
// Default for stereo is HRTF
unsigned short panningModel;
// Uses a 3D cartesian coordinate system
void setPosition( float x, float y, float z );
void setOrientation( float x, float y, float z );
void setVelocity( float x, float y, float z );
// Directional sound cone
float coneInnerAngle;
float coneOuterAngle;
float coneOuterGain;
}
AudioPannerNode - Basic Panning
// Create the panning node
var panner = audioContext.createPanner();
// default to straight ahead
panner.setPosition(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
panner.connect( audioContext.destination );
...
// remember, 0.0 is straight ahead: negative=left, positive=right
panner.setPosition( newPanningPosition, 1.0, 0.0 );
AudioPannerNode
This is also how you get Doppler effects
AudioListener
interface AudioListener {
void setPosition( float x, float y, float z );
void setOrientation( float x, float y, float z, float xUp, float yUp, float zUp );
void setVelocity( float x, float y, float z );
}
audioContext.listener.setVelocity(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); // Up, up and away!

ConvolverNode
- Convolution reverb digitally simulates a physical or virtual space.
- Provides room ambience, also emulates any electronic or analog processor
- Uses Impulse Response files - lots available on the net
- Again, remember the output is ONLY the processed signal!
interface ConvolverNode : AudioNode {
// buffer is the impulse response file
AudioBuffer buffer;
boolean normalize;
}
ConvolverNode
Impulse Response files are just another sound buffer!
var drums = audioContext.createBufferSource(); drums.buffer = drumsBuffer; drums.loop = true; var convolver = audioContext.createConvolver(); convolver.buffer = hallImpulseResponseBuffer; drums.connect( convolver ); drums.connect( audioContext.destination ); convolver.connect( audioContext.destination ); drums.noteOn(0);
Using Web Audio for Synthesis
Web Audio can also provide sources of sound and musical effects
OscillatorNode
Anti-aliased periodic waveform source (Also useful for AudioParam inputs!)
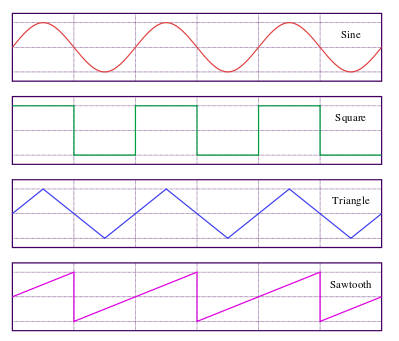
interface Oscillator : AudioSourceNode {
const SINE = 0, SQUARE = 1, SAWTOOTH = 2,
TRIANGLE = 3, CUSTOM = 4;
unsigned short type;
AudioParam frequency; // in Hertz
AudioParam detune; // in Cents
void noteOn( double when );
void noteOff( double when );
void setWaveTable( WaveTable waveTable );
}
WaveTable
- Complex waveforms created from Fourier series harmonic coefficients
var wavetable = audioContext.createWaveTable( Float32Array real, Float32Array imag ); oscillator.setWaveTable( wavetable );
DynamicsCompressor - Pump Up the Volume!
interface DynamicsCompressorNode : AudioNode {
AudioParam threshold; // in Decibels
AudioParam knee; // in Decibels
AudioParam ratio; // unit-less
AudioParam attack; // in Seconds
AudioParam release; // in Seconds
}
DynamicsCompressorNode
WaveShaper
WaveShaper performs non-linear distortion effects with an arbitrary curve- useful for overdrive, soft clipping, and bit-crushing.
interface WaveShaperNode : AudioNode {
Float32Array curve;
}
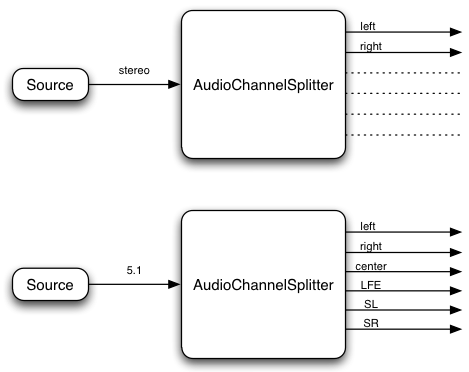
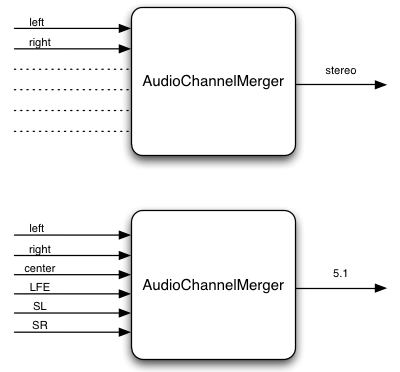
Splitting and Merging Channels in a Connection
AudioChannelSplitter/Merger give access to individual channels.
Ping-Pong!
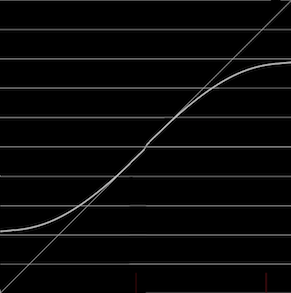
var ppMerger = audioContext.createChannelMerger(); // Create independent delays (can have different delayTimes if desired) var ppLeftDelay = audioContext.createDelayNode(); var ppRightDelay = audioContext.createDelayNode(); ppLeftDelay.delayTime.value = 0.3; ppRightDelay.delayTime.value = 0.3; // Gain nodes so the echoes fade over time var ppLeftFeedback = audioContext.createGainNode(); var ppRightFeedback = audioContext.createGainNode(); ppLeftFeedback.gain.value = 0.65; ppRightFeedback.gain.value = 0.65; // Connect left into right, and right into left ppLeftDelay.connect(ppLeftFeedback); ppLeftFeedback.connect(ppRightDelay); ppRightDelay.connect(ppRightFeedback); ppRightFeedback.connect(ppLeftDelay); // Merge the two delay channels into stereo L/R ppLeftFeedback.connect(ppMerger, 0, 0); ppRightFeedback.connect(ppMerger, 0, 1); ppMerger.connect( audioContext.destination);
JavaScriptAudioNode
We can do audio processing and synthesis directly in JavaScript, too.
interface JavaScriptAudioNode : AudioNode {
EventListener onaudioprocess;
long bufferSize;
}
interface AudioProcessingEvent : Event {
JavaScriptAudioNode node;
float playbackTime;
AudioBuffer inputBuffer;
AudioBuffer outputBuffer;
}
Web Audio Status
- Supported in Chrome on Windows, Mac OS X, Linux
- ChromeOS just enabled April 2012
- Apple Safari - Enabled in nightly builds, shipping in Safari 5.2 beta
- Now in iOS6 betas too!
- W3C audio working group work continues - in 2nd public working draft, Active participation in WG from Mozilla, Opera and others
- ChromeFrame!!
The Future
- Two REALLY exciting upcoming features:
- Audio input via getUserMedia()
- MIDI input for live controller input
- Awesome apps I want you all to build...
- Rich interactive sound in game engines
- Shared music composition
- Digital Audio Workstations
- DJ performance tools
- Software Synthesizers
- Software sequencers and performance instruments
- Audio “effects boxes”
References
- This deck: http://webaudio-io2012.appspot.com/
- Specification:
https://dvcs.w3.org/hg/audio/raw-file/tip/webaudio/specification.html - HTML5 Rocks Intro Tutorial: http://www.html5rocks.com/en/tutorials/webaudio/intro/
- Web Audio Demos: http://chromium.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/samples/audio/index.html
- Vocoder demo:
webaudiovocoder.appspot.com, github.com/cwilso/Vocoder - Web Audio Playground:
webaudioplayground.appspot.com, github.com/cwilso/WebAudio - Using Web Audio for Gaming:
http://www.html5rocks.com/en/tutorials/webaudio/games/
<Thank You!>
This deck: goo.gl/lX1DV
